The Means by Which a Pathogenic Organism Invades the Body
Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapted and endowed with mechanisms for overcoming the normal body defences and can invade parts of the body such as the blood where bacteria are not normally found. These infectious bugs are typically considered as deadly.
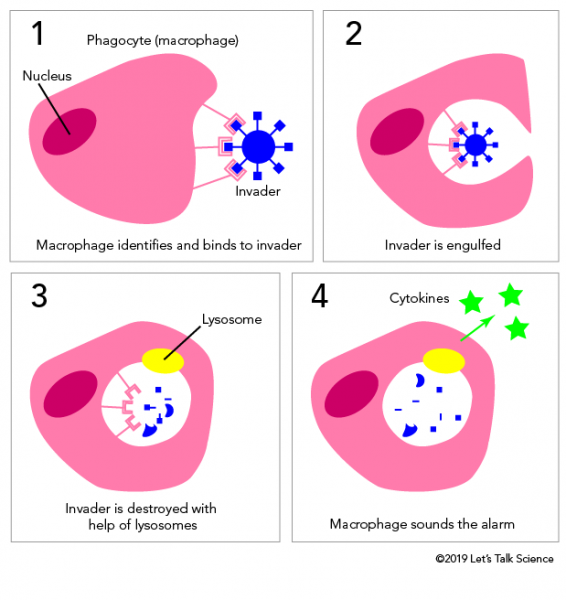
The Immune Response Let S Talk Science
Medicine the invasion of the body by pathogenic microorganisms and their multiplication which can lead to tissue damage and disease.

. The antibodies destroy the antigen pathogen which is then engulfed and digested by macrophages. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapted and endowed with mechanisms for overcoming the normal body defences and can invade parts of the body such as the blood where bacteria are not normally found. The epithelium of the small intestine is composed of absorptive enterocytes mucus-producing goblet cells M cells as well as proliferating stem cells and Paneth cells located in intestinal crypts.
A microbe that is capable of causing disease is referred to as a pathogen while the organism being infected is called a hostThe ability to cause disease is referred to as pathogenicity with pathogens varying in their abilityAn opportunistic pathogen is a microbe that typically infects a host that is compromised in some way either by a weakened. For this anti-biotic medication is used to treat bacterial infection. Invasion Pathogenic bacteria invades the cells of the body while nonpathogenic bacteria live outside the body cells.
They do so either by direct transmission from one cell to the next or by release into the extracellular fluid and reinfection of both adjacent and distant cells. Pathogenic bacteria adhere to the cells of the tissues in order to escape from the fluid flows inside the body while nonpathogenic bacteria do not adhere to the tissue. Invasion of the body by a microorganism is called infection.
A type of virus capable of causing illness is bacteria. Some pathogens exist as air borne particles. They can also be introduced into foods during processing from the air unclean hands insanitary utensils and.
Bacteria are generally less tissue-specific and non-discriminatory than viruses and can make a range of infections after they have invaded the host. 21 Bacterial Pathogenicity. Harmful bacteria that can cause infections are called pathogenic bacteria.
Many common food poisoning organisms cause pathology without spreading into. The body can be more vulnerable to bacterial infection when your immune system is invaded by a virus rendering harmless bacteria pathogenic. Bacteria and viruses multiply on or in the epithelial surface causing localized disease.
Specifically an intraphagocytic pathogen can alter the way in which the immune system works. A number of these bacteria will occupy residence in the human body and help develop a robust immune system. White blood cells can also produce chemicals called antitoxins which destroy the toxins poisons some bacteria produce when they have invaded the body.
Routes of invasion by enteric pathogens in the human small intestine. For instance the ability of a bacteria to invade a cell or tissue to establish an infection within the body and to avoid or even exploit the immune response is often dependent on the bacterias ability to manipulate the host cytoskeleton and exploit various biochemical pathways that respond to changes in mechanical stimuli. What Is An Example Of A Pathogenic.
A pathogens is an infectious species of microscopic organisms with the ability to survive reproduce and colonize. As with any organism pathogens prioritize survival and reproduction. Phonetics the alteration of a speech sound under the influence of a neighboring sound.
Pathogenic bacteria can enter the process on raw materials. Pathogens must spread from cell to cell. The severity of the disease state depends upon its virulence.
An incident in which an infectious disease is transmitted. The most common type of pathogens are bacteria viruses and fungi. A pathogen is defined as an infectious microorganism present in the natural environments that can infect or invades the body and causes the disease to its host.
The human bodys immune system acts as a defense. Another name for a pathogen is an infectious agent as they cause infections. The process of conferring resistance to a pathogen by the administration of a vaccine is called immunization Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a harmless substance as if it were a harmful pathogen.
It can be cellular such as bacteria protozoa parasites fungi or acellular such as virus and prion. Pathogens are of different types and they can spread by various means but most commonly they spread by means of skin contact or while transferring body fluids or through contaminated surface contacting. Others have specialized virulence factors and strategies that allow them to invade across the epithelial cell surface local invasion or invade across the epthelial cell surface and spread systemically through the body.
Antigens are proteins that are found on the surface of the pathogen. Humans and small organisms organisms called pathogens or germs are prone to developing infectious diseasesA person who has come into contact with an infected area of the body knows they are infectedViruses bacteria fungi and protozoans are known to cause illnessColds influenza the flu chicken pox measles and AIDS are a few Viruses that cause.
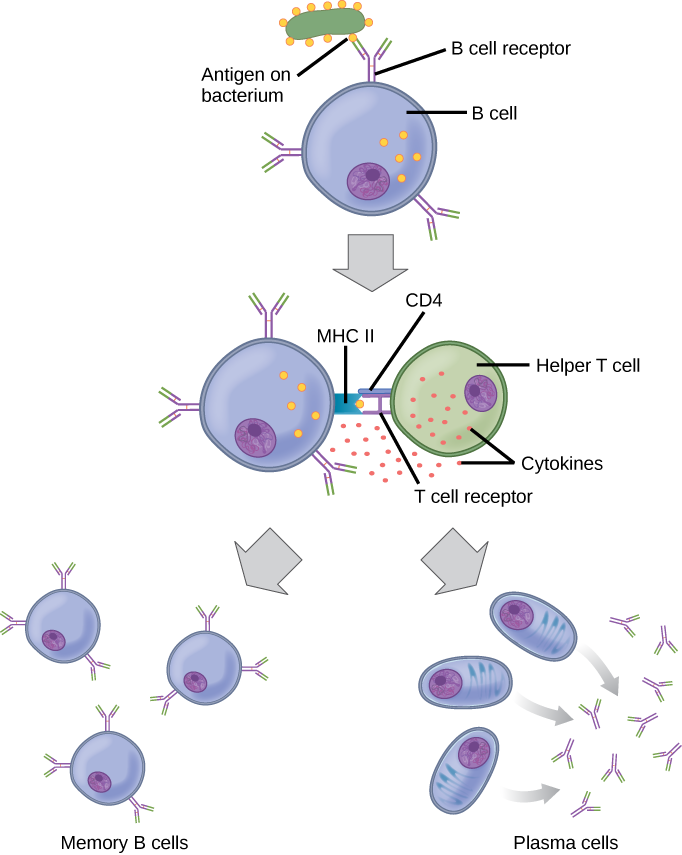
The Immune System Review Article Khan Academy

Ijms Free Full Text Metagenomics A New Way To Illustrate The Crosstalk Between Infectious Diseases And Host Microbiome Html

The Immune System Ppt Download

Antigens Antibodies 10 2 1 Cie Igcse Biology Revision Notes 2020 Save My Exams

How Pathogens Cause Disease Microbiology
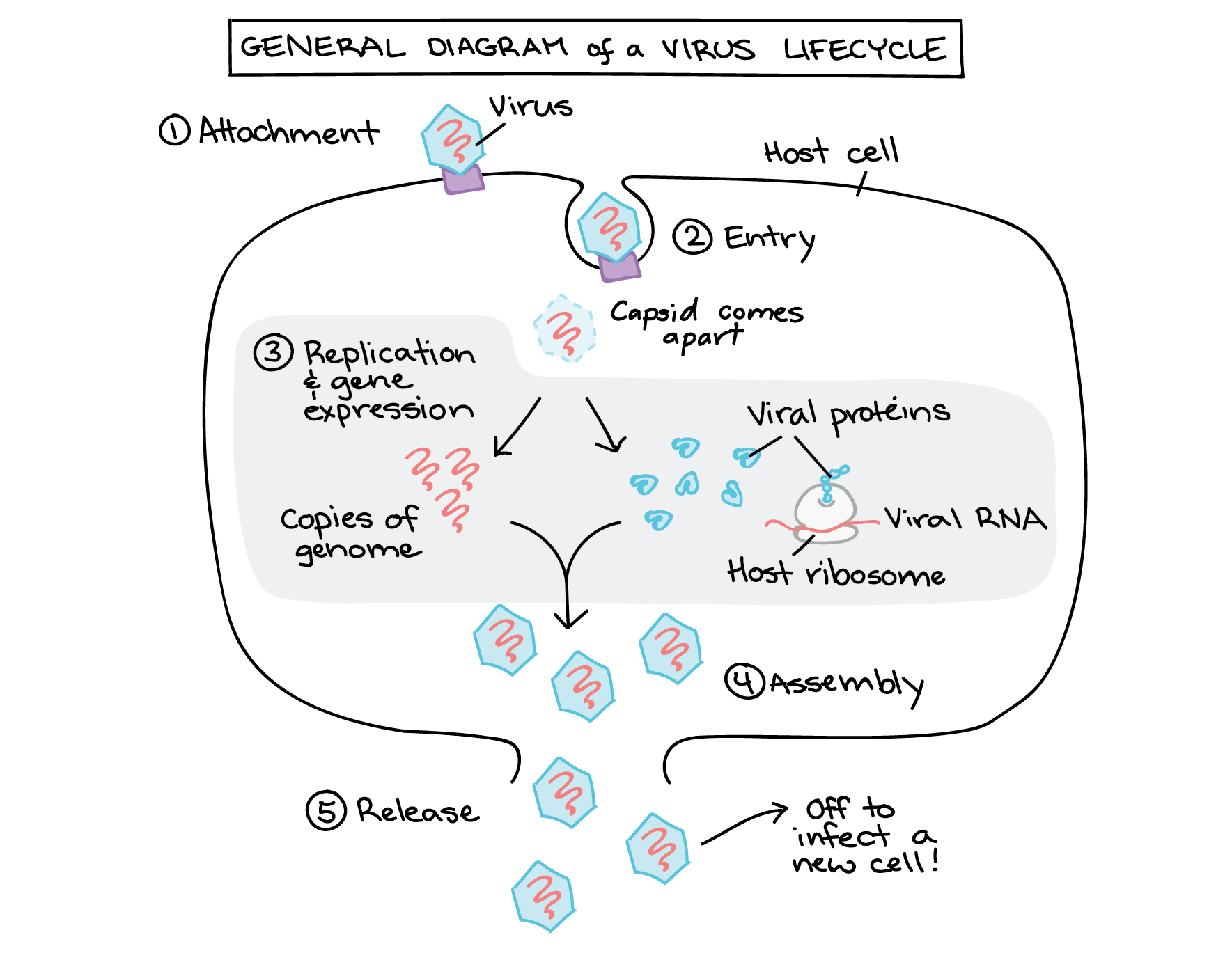
The Immune System Review Article Khan Academy

Innate Immune Response Boundless Biology

An Introduction To Infectious Disease Science In The News
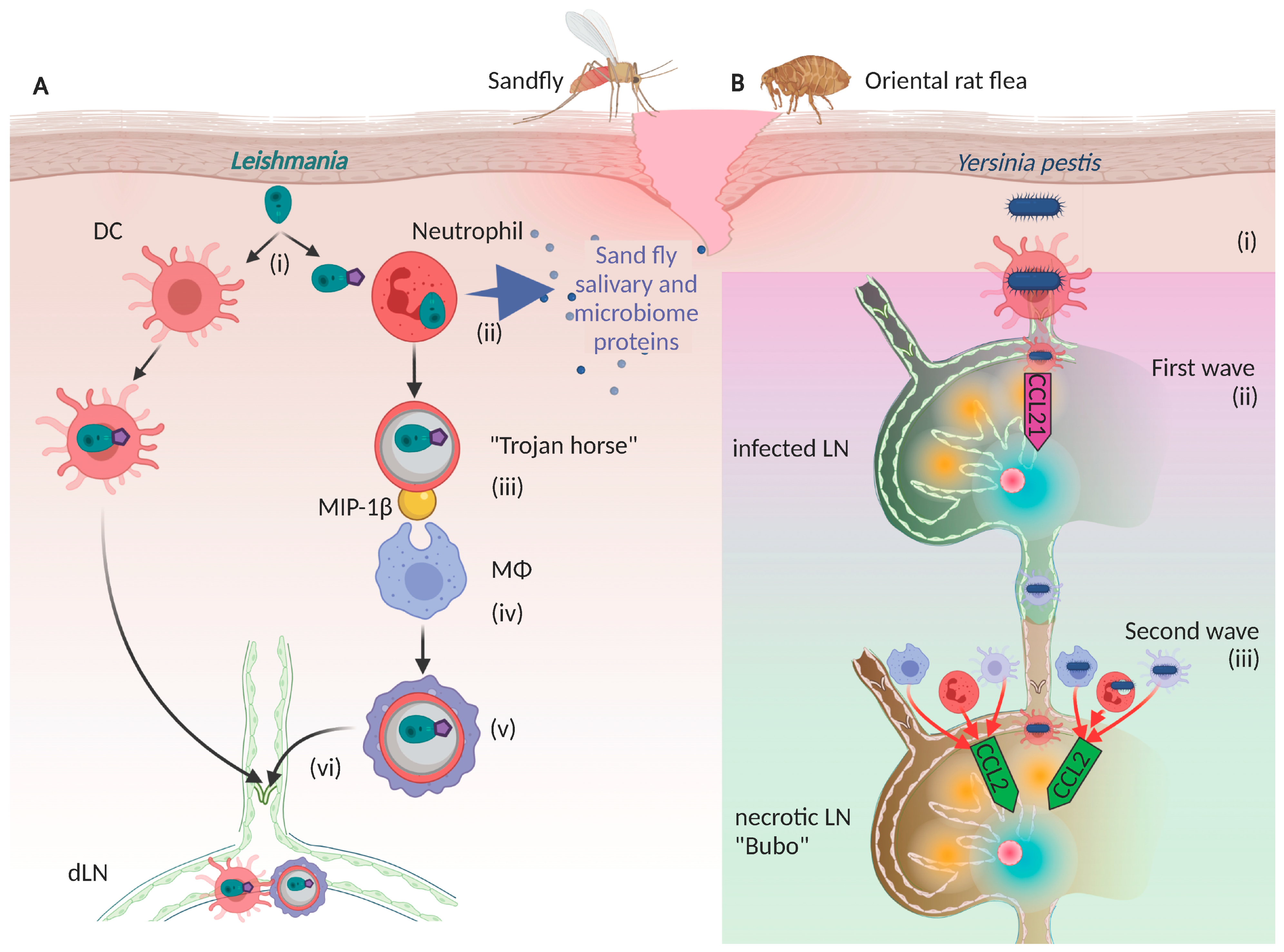
Cells Free Full Text Pathogenic Exploitation Of Lymphatic Vessels Html

Antigens Antibodies 10 2 1 Cie Igcse Biology Revision Notes 2020 Save My Exams
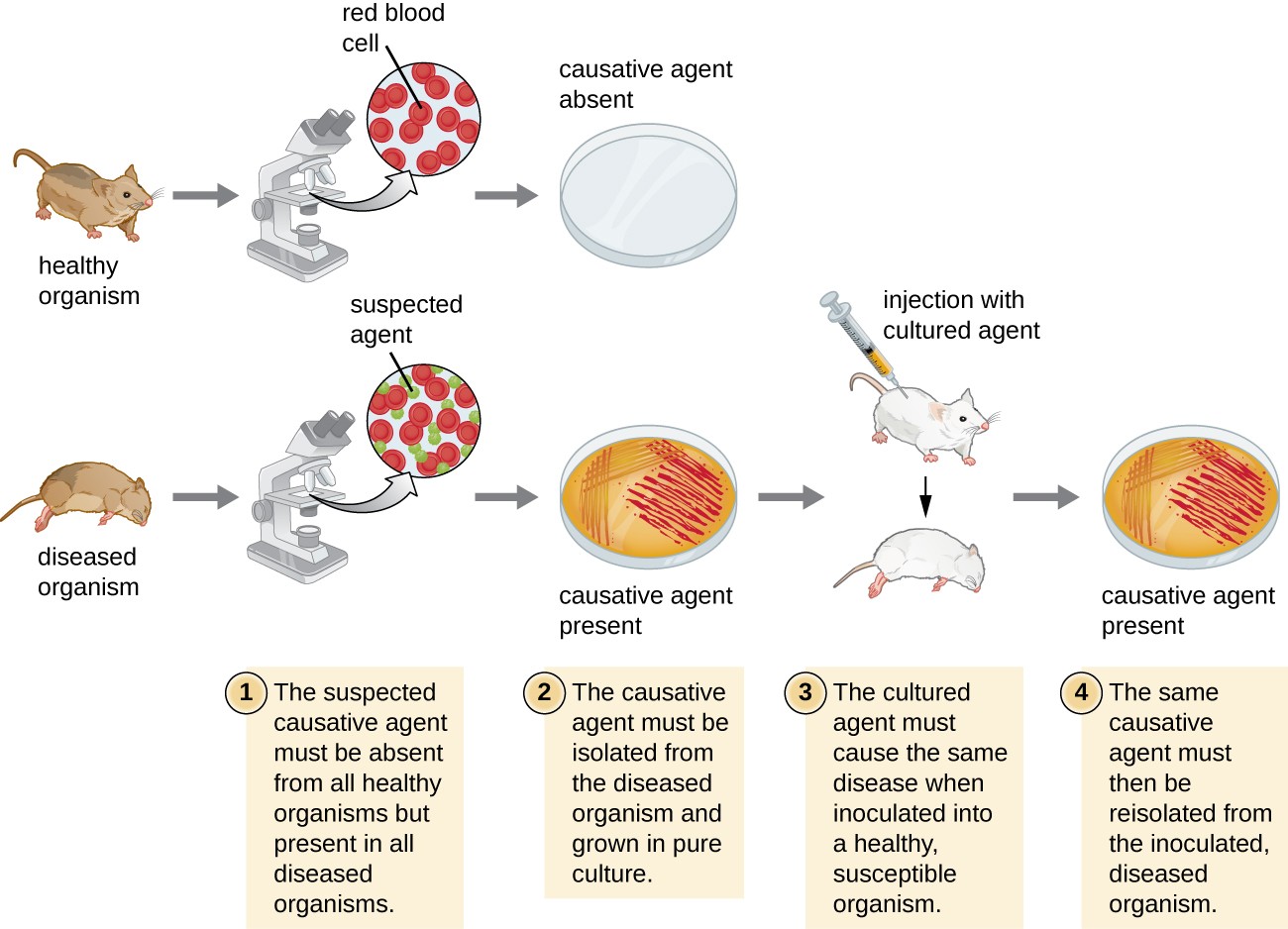
How Pathogens Cause Disease Microbiology
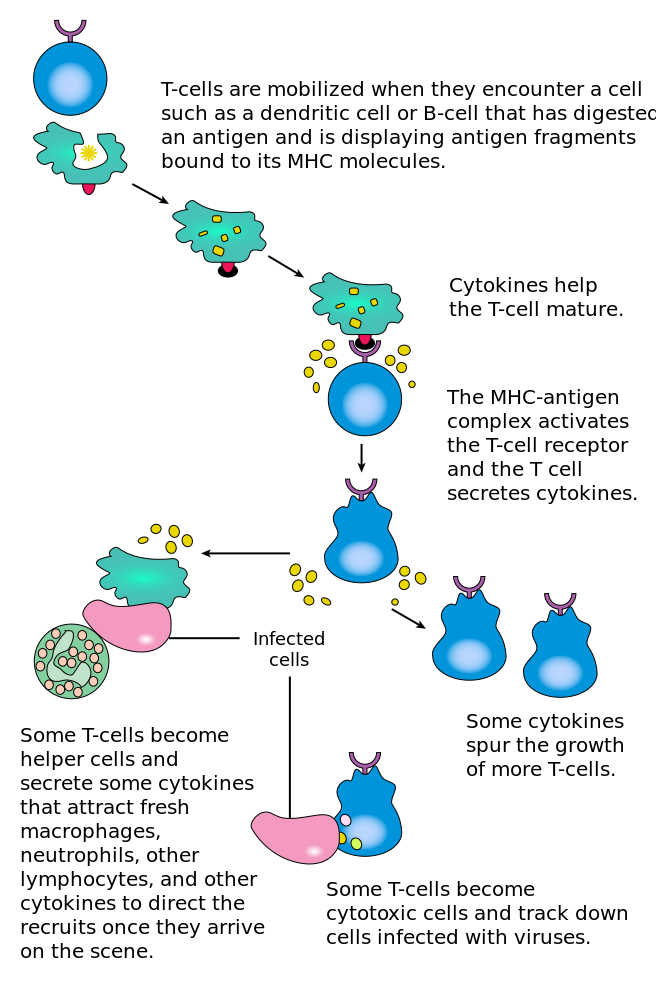
The Immune System Review Article Khan Academy
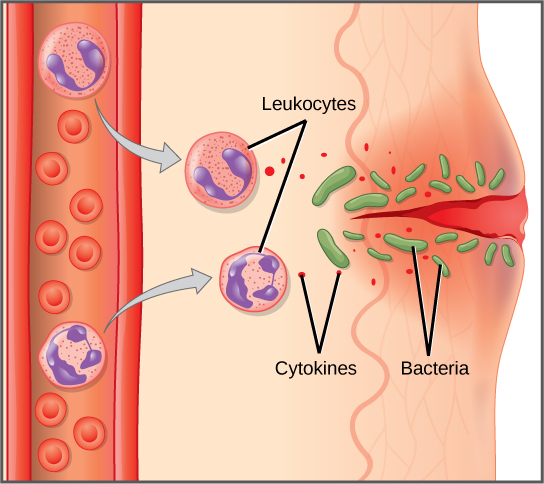
The Immune System Review Article Khan Academy
Biofilms By Bacterial Human Pathogens Clinical Relevance Development Composition And Regulation Therapeutical Strategies
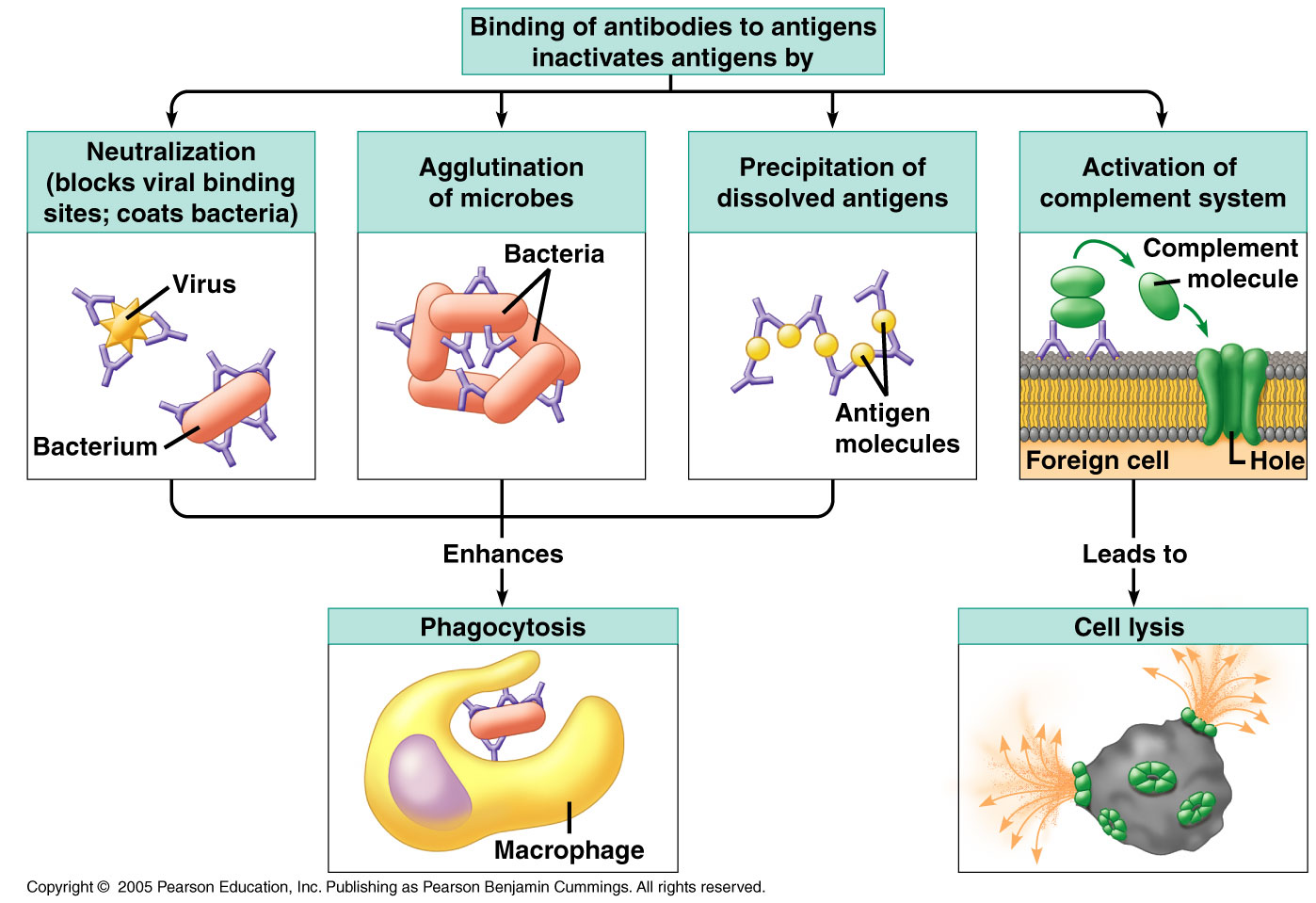

Comments
Post a Comment